Moab City How to Read Water Bill

The offset step in irresolute the way you use water in the future is by understanding how much water you utilise today. The best identify to notice this information is on your monthly water bill. Pull out your water bill and follow the steps below to larn more nigh information technology and your own water utilize.
On This Page:
- How much practise you employ?
- What is your usage trend?
- How does your utilise compare to that of your neighbour?
- How are you being charged?
- What are my charges going towards?
- More Information
How much do yous utilize?

Different utilities use different units for measuring water use. The well-nigh common units are centum cubic feet (CCF) and the gallon. A CCF also called an HCF (hundred cubic anxiety), represents 1 hundred cubic feet of h2o. The first "C" comes from the Roman word for hundred, "centum." This is the well-nigh common unit used by both h2o and natural gas utilities. But you may exist more than familiar with the other unit, the gallon. Ane CCF is equal to 748 gallons.
What does your usage mean? The average American uses around 88 gallons per day per person in the household. That ways a family of 4 would utilize around 10,500 gallons in a 30-solar day period. But usage varies a great deal across the state, mostly considering of differences in weather patterns. For example, h2o apply tends to exist higher in drier areas of the country that rely more than on irrigation for outdoor watering than in wetter parts of the country that can rely on more rainfall.
Based on information from H2o Research Foundation, "Residential End Uses of Water, Version 2." 2016; and The US Geological Survey, "Estimated Water Use in the United States." 2010.
What is your usage trend?
Does your bill explain your household's usage trend? Some utilities provide graphs similar the ones below that prove how your water apply has varied over the course of the year and previous years. This can exist a helpful way of seeing when your own water use reaches its highest levels.

While using water efficiently is important throughout the year, sometimes the timing of water utilise can make a big difference for community water supplies—and your water bill. WaterSense has tips to help you reduce your water use when it'southward hot outside.
Water utilities operate with this higher, summertime employ in mind because they must be able to provide for all the water a customs needs over an extended period. Some systems may be forced to restrict outdoor watering during the peak to ensure that water is available for more than important community needs.
How does your apply compare to that of your neighbor?
Some utilities provide information on how your household compares to that of your neighbors. This can assist yous come across how your usages stacks up versus other users in your same climate surface area and tin be a helpful way of gauging your "WaterSense." Some utilities use bills that compare your utilise to a random grouping of your neighbors while some utilities use a "tiered system" to differentiate users such as in the example below.

How are yous being charged?
Water utilities need to charge customers to build and maintain infrastructure—the water storage tanks, handling plants, and underground pipes that evangelize water to homes and businesses. The acquirement is also used to pay the workers who provide yous with water service twenty-four hour period or night. There are a wide diversity of charge per unit structures that are used to bill customers, some of which are described below.
Rate Types
Flat Fee is a rate structure where all customers are charged the same fee, regardless of the amount of water used. Flat fees are the simplest type of rate structure and are rarely used today. They generally don't provide revenue sufficient to operate the utility and are not practiced at promoting water efficiency.

Uniform Rate is a structure that has a constant per unit price for all metered units of water consumed on a yr-round ground. Information technology differs from a flat fee in that it requires metered service. Some utilities accuse varying user groups different rates such as charging residential households ane rate and industrial users a different charge per unit. Constant block rates provide some stability for utilities and encourage conservation considering the consumer bill varies with water usage.

Increasing Cake Rates is a rate structure in which the unit price of each succeeding cake of usage is charged at a higher unit rate than the previous cake(s). Increasing block rates are designed to promote conservation and are most oft found in urban areas and areas with express water supplies. The graphic to the right is an example of an increasing block rate structure.

Declining Block Rates are the opposite of increasing block rates where the unit price of each succeeding block of usage is charged at a lower unit of measurement rate than the previous cake(s). This rate structures are popular in rural areas that service large farming populations or areas with large users such as heavy manufacture and where water is plentiful.
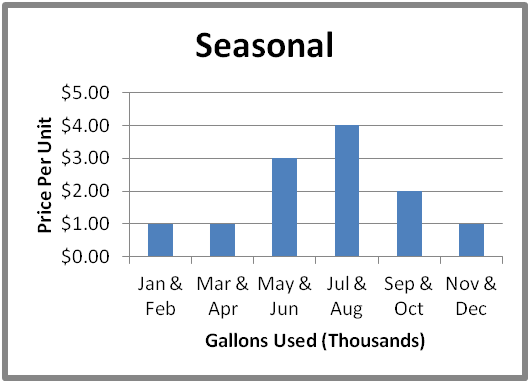
Seasonal Rates are rates that comprehend a specific time catamenia. They are established to encourage conservation during peak use periods. Examples of seasonal rates may have lower rates for the winter season and higher rates for the summer season due to increased water demand associated with lawn watering and outside activities.

Drought Rates are similar to seasonal rates but instead of applying higher rates during an entire time menses, they conform rates based on the local area'southward drought level. Higher levels of drought result in higher prices for h2o in order to encourage conservation.

Water Budget Based Rates is a rate construction where households are given a "water budget" based on the anticipated needs of that household either by the number of people living in the firm and/or property size. Users are charged a certain rate for use within their budget and a higher rate for employ that exceeds their budget. The goal is to encourage efficient water apply of every individual customer.
What are my charges going towards?
Many utilities apply a combination of a stock-still fee (base) and a variable fee (volume) for their h2o rate construction. Fixed charges generally include the price the customer pays as a base of operations charge to assist encompass costs for maintaining existing infrastructure and repaying loans and bonds used to build that infrastructure. Variable charges are the price the client pays per volume of h2o used, which reverberate the costs of providing water, such equally costs for chemical treatment to provide safe water and free energy to movement and deliver water.
Nigh utilities will provide you with a breakdown of charges in your "billing particular" or "summary of charges" department. Notation that some utilities measure both water inbound the house and waste matter leaving to the sewer, but many utilities have only one meter on location and will charge both volumes based on h2o entering the house. This is nonetheless another reason to reduce your ain water utilise. If you're curious almost what various surcharges and other charges on your utility bill mean, you can usually find that data either on the back or appendix of the bill or on your local water utility's website. Two examples are provided below.

Compatible Rate Example - in the offset example, roughly half of the $147.62 being charged is directly related to h2o use. Most utilities charge a fix flat fee (the "Water Base Facility Charge" in the example) that helps to pay for the base costs of providing water including the electricity needed to send and make clean the water, the personnel and others costs of daily maintenance of the delivery organisation, and other stock-still operating costs.
This utility uses a compatible rate structure that charges the user $0.00295 per gallon (or roughly 3 cents for every 10 gallons) used during the billing period. The bill also shows a similar facility charge for sewer and a "charge per unit case expense surcharge" to help pay for the utility'due south rate setting process. The "regulatory assessment fee" helps the utility pay for costs associated with maintaining regulatory compliance with clean water statutes. Finally, some utilities charge fees similar to the "Deferred Capital Expense Surcharge" which puts money into a fund to help pay for long term investments in improvements to infrastructure such every bit new pipes, treatment facilities or reservoirs.

Increasing Cake Rate Example - this 2nd bill is an instance of an efficient user with an increasing block rate structure. Yous can see that the utility has fifty-fifty labeled the various blocks with its corresponding water employ efficiency level. The above user falls into the "Efficient" group and so avoids the much higher per unit costs of the next iii tiers. Some utilities will forgive various surcharges for its about efficient users because their below average water apply places less burden on the system and reduces need for new sources of water and pipes to transport this water.
More Information
Utilities will oft use the back of the bill as a "bulletin area." This surface area volition sometimes accept data on rebate programs, water efficient products, or other tips on h2o conservation.
If you're looking for more data on how your neb functions, you can visit the following sites:
- For interactive examples of bills visit Agreement your Water Pecker pages from the Eastward Bay Municipal Bay Utility District (CA) and Cleveland (OH) Water.
- To larn more nigh what services are existence paid for from water bills, visit the Financing Sustainable Water page for concerned citizens.
- For an example of an interactive, comparative utility bill, visit WaterSmart Software.
Source: https://www.epa.gov/watersense/understanding-your-water-bill
0 Response to "Moab City How to Read Water Bill"
Post a Comment